Note
Click here to download the full example code
Hartmann functions¶
Hello world
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from scipy.optimize import minimize
from etudes.decorators import value_and_gradient, numpy_io
num_iterations = 50000
num_runs = 100
seed = 886 # set random seed for reproducibility
random_state = np.random.RandomState(seed)
alpha = np.array([1.0, 1.2, 3.0, 3.2])
A = {}
A[3] = np.array([[3.0, 10.0, 30.0],
[0.1, 10.0, 35.0],
[3.0, 10.0, 30.0],
[0.1, 10.0, 35.0]])
A[6] = np.array([[10.0, 3.0, 17.0, 3.5, 1.7, 8.0],
[0.05, 10.0, 17.0, 0.1, 8.0, 14.0],
[3.0, 3.5, 1.7, 10.0, 17.0, 8.0],
[17.0, 8.0, 0.05, 10.0, 0.1, 14.0]])
A[4] = A[6].T
P = {}
P[3] = 1e-4 * np.array([[3689, 1170, 2673],
[4699, 4387, 7470],
[1091, 8732, 5547],
[381, 5743, 8828]])
P[6] = 1e-4 * np.array([[1312, 1696, 5569, 124, 8283, 5886],
[2329, 4135, 8307, 3736, 1004, 9991],
[2348, 1451, 3522, 2883, 3047, 6650],
[4047, 8828, 8732, 5743, 1091, 381]])
P[4] = P[6].T
x_min = {}
x_min[3] = np.array([0.114614, 0.555649, 0.852547])
x_min[6] = np.array([0.20169, 0.150011, 0.476874, 0.275332, 0.311652, 0.6573])
axis = {}
axis[3] = -1
axis[6] = -1
axis[4] = -2
a = {}
a[3] = 0.0
a[4] = 1.1
a[6] = 0.0
b = {}
b[3] = 1.0
b[4] = 0.839
b[6] = 1.0
def make_hartmann_tf(alpha, A, P, a=0.0, b=1.0, axis=-1):
@numpy_io
@value_and_gradient
def hartmann(x):
r = tf.reduce_sum(A * tf.square(x - P), axis=axis)
return (a - tf.reduce_sum(alpha * tf.exp(-r), axis=-1)) / b
return hartmann
hartmann4d = make_hartmann_tf(alpha, A[4], P[4], a[4], b[4], axis[4])
Starting point
x_init = random_state.rand(4)
x_init
Out:
array([0.00140876, 0.75240707, 0.10057118, 0.4699249 ])
res = minimize(hartmann4d, x0=x_init, jac=True, method="L-BFGS-B", tol=1e-8)
res
Out:
fun: -0.1182632861801847
hess_inv: <4x4 LbfgsInvHessProduct with dtype=float64>
jac: array([-2.38112332e-07, 6.28465891e-07, 1.22074520e-05, 1.61916050e-06])
message: b'CONVERGENCE: REL_REDUCTION_OF_F_<=_FACTR*EPSMCH'
nfev: 42
nit: 27
status: 0
success: True
x: array([0.40389835, 0.67337835, 0.35171053, 0.41247776])
x_min[4] = res.x
def make_hartmann(alpha, A, P, a=0.0, b=1.0, axis=-1):
def hartmann(x):
r = np.sum(A * np.square(x - P), axis=axis)
return (a - np.dot(np.exp(-r), alpha)) / b
return hartmann
frames = []
for dim in [3, 4, 6]:
hartmann = make_hartmann(alpha, A[dim], P[dim], a[dim], b[dim], axis[dim])
xs = random_state.rand(num_runs, num_iterations, 1, dim)
ys = hartmann(xs)
y_min = hartmann(x_min[dim])
df = pd.DataFrame(np.minimum.accumulate(np.abs(y_min - ys), axis=1))
df.index.name = "run"
df.columns.name = "iteration"
s = df.stack()
s.name = "regret"
frame = s.reset_index()
frames.append(frame.assign(name=f"Hartmann {dim}D"))
data = pd.concat(frames, axis="index", sort=True)
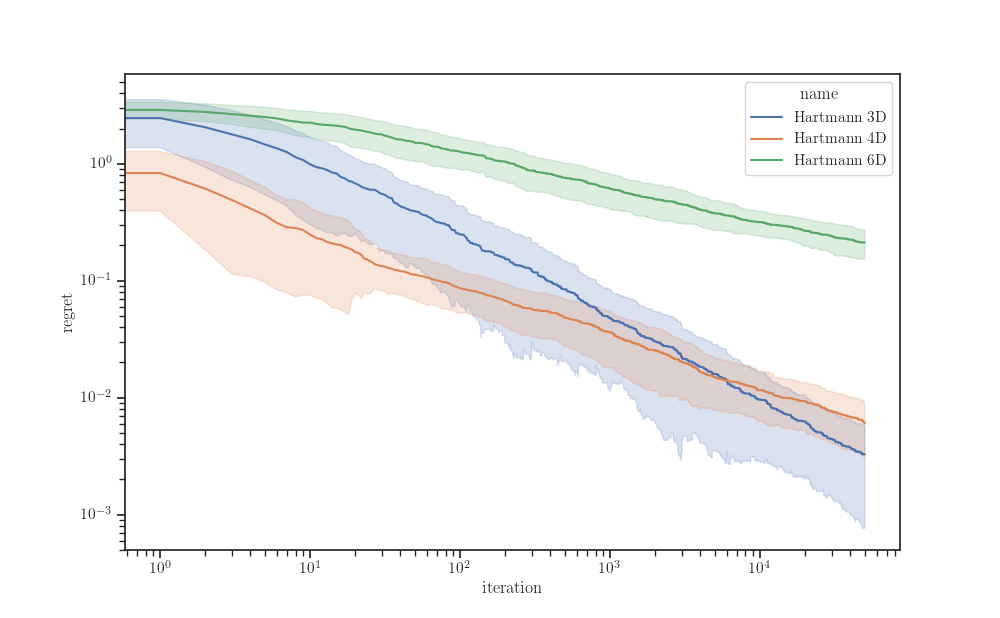
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
sns.lineplot(x="iteration", y="regret", hue="name",
# units="run", estimator=None,
ci="sd", palette="deep", data=data, ax=ax)
ax.set_xscale("log")
ax.set_yscale("log")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 27.213 seconds)